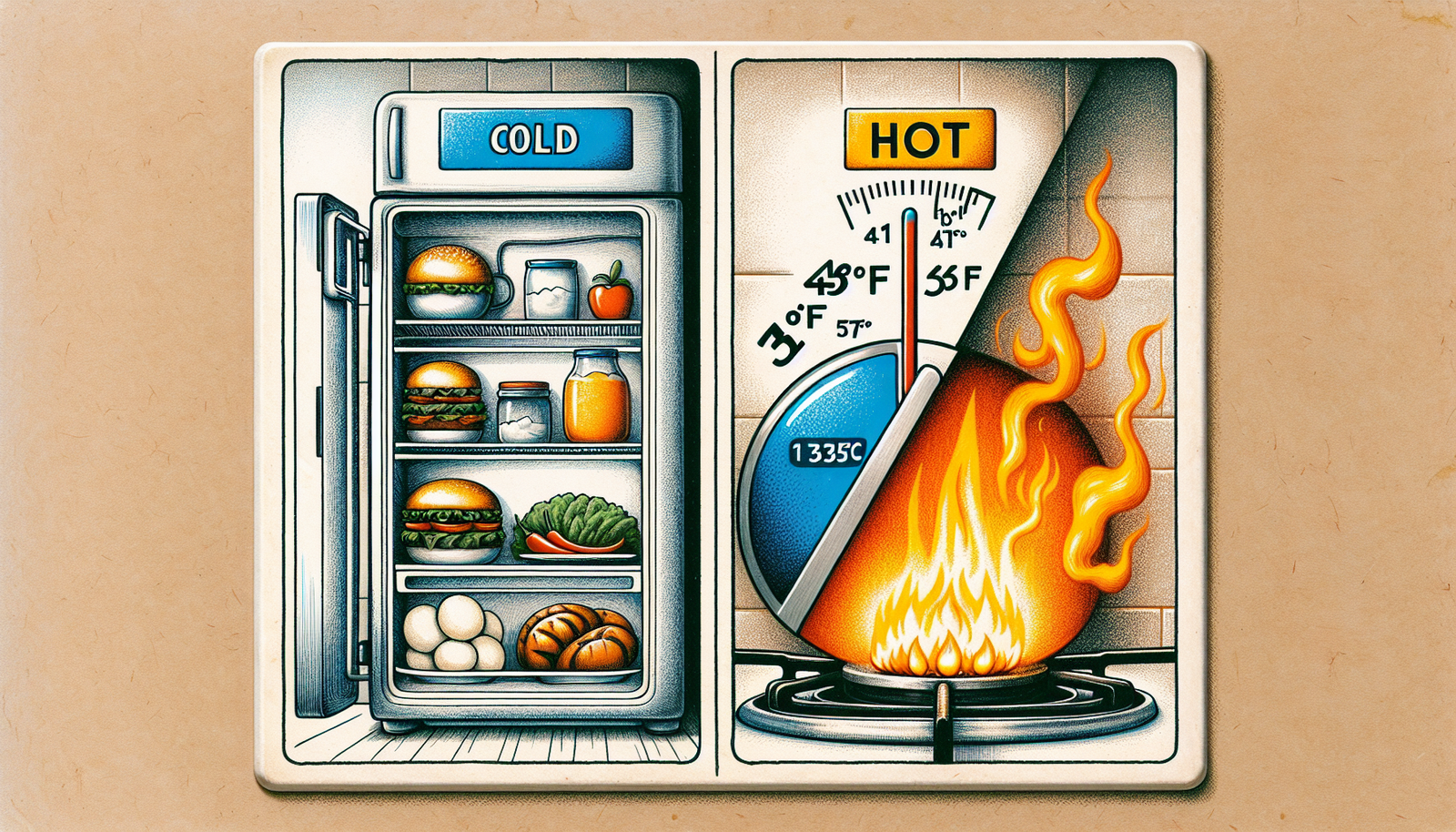
In the world of food safety, it’s crucial to understand the temperature danger zone as outlined by the FDA food Code. This zone refers to the range of temperatures in which bacteria can grow rapidly, potentially leading to foodborne illnesses. By knowing and adhering to these temperature guidelines, you can ensure the safety and quality of the food you handle. Let’s explore the temperature danger zone and discover how it impacts our daily culinary practices.
Temperature Danger Zone Defined
Definition of temperature danger zone
The temperature danger zone refers to a specific temperature range in which harmful bacteria can rapidly grow and multiply on food, posing a significant risk to human health. According to the FDA Food Code, the temperature danger zone is between 41°F (5°C) and 135°F (57°C).
Importance of maintaining proper food temperatures
Maintaining proper food temperatures is crucial for ensuring food safety and preventing the proliferation of harmful bacteria. By keeping food outside of the temperature danger zone, you reduce the risk of foodborne illnesses, protect the health of consumers, and safeguard the reputation and success of businesses in the food industry.
FDA Food Code Guidelines
Overview of the FDA Food Code
The FDA Food Code is a set of model regulations and guidelines developed by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to provide uniformity in food safety standards across the country. It covers various aspects of food handling, including temperature control, to minimize the risk of foodborne illnesses.
Role in establishing food safety regulations
The FDA Food Code serves as a valuable resource for regulatory agencies, industry professionals, and food establishments in implementing and enforcing food safety regulations. By following the guidelines outlined in the Food Code, businesses can ensure compliance with federal, state, and local regulations, promoting a safer food supply chain.
Scope and applicability
The FDA Food Code is applicable to all types of food service establishments, including restaurants, cafes, delis, schools, and hospitals. It provides comprehensive guidance on various aspects of food safety, including temperature control, proper cooking and holding temperatures, and monitoring procedures.
Temperature Danger Zone Range
Specific temperature range defined
The temperature danger zone range, as defined by the FDA Food Code, starts at 41°F (5°C) and extends up to 135°F (57°C). Within this range, bacteria can multiply rapidly, increasing the risk of foodborne illnesses. It is essential to keep foods either below or above this range to prevent bacterial growth.
Factors contributing to bacterial growth
Bacterial growth is influenced by various factors, including temperature, moisture, pH levels, and the availability of nutrients. The temperature danger zone provides an ideal environment for bacterial multiplication, as it allows bacteria to double in number every 20 minutes, leading to a potential outbreak of foodborne illnesses.
Impact on food safety
Allowing food to remain within the temperature danger zone for an extended period significantly compromises food safety. Bacteria such as Salmonella, E. coli, and Campylobacter thrive in this range and can cause severe illnesses if consumed. To ensure food safety, it is crucial to implement effective temperature control measures throughout the food production and handling process.
Health Risks and Concerns
Bacterial growth and multiplication
When food is stored or held in the temperature danger zone, bacteria present on the food can multiply rapidly. This can lead to a significant increase in the bacterial load, making the food unsafe to consume. Proper temperature control measures are necessary to prevent bacterial growth during storage, preparation, and service.
Pathogens commonly associated with improper temperature control
Several pathogens are commonly associated with unsafe food temperatures. Salmonella, commonly found in raw poultry and eggs, can cause severe gastrointestinal illness. E. coli, found in undercooked ground beef or contaminated produce, can lead to symptoms like diarrhea and kidney failure. Campylobacter, often found in raw or undercooked poultry, can also cause gastrointestinal issues.
Foodborne illnesses and their consequences
Improper temperature control can result in foodborne illnesses, with symptoms ranging from mild discomfort to life-threatening conditions. These illnesses can lead to hospitalization, long-term health complications, and in severe cases, even death. Pregnant women, young children, the elderly, and individuals with weakened immune systems are particularly vulnerable to the health risks posed by foodborne illnesses.
Vulnerable population groups
Certain population groups are more susceptible to the adverse effects of foodborne illnesses. Pregnant women are at risk of miscarriage, premature delivery, or stillbirth if exposed to certain pathogens. Infants, young children, and the elderly have weaker immune systems, making them more prone to severe symptoms and complications from foodborne illnesses.
Foodborne Illness Incidents
Examples of foodborne illness outbreaks
Several well-known outbreaks have been linked to improper temperature control. In 1993, the Jack in the Box E. coli outbreak resulted in multiple deaths and severe illnesses. In 2011, a listeria outbreak linked to contaminated cantaloupes caused numerous fatalities. These incidents serve as reminders of the importance of strict temperature control measures.
Causes attributed to temperature abuse
Temperature abuse, such as failure to maintain proper hot or cold holding temperatures, can occur due to various reasons. Inadequate refrigeration or heating equipment, improper cooling or reheating methods, and insufficient staff training can all contribute to temperature abuse, leading to the proliferation of bacteria and subsequent foodborne illnesses.
Consequences for businesses
Foodborne illness outbreaks can have severe consequences for businesses. Beyond the potential legal ramifications and damage to reputation, outbreaks can lead to financial losses, closure, and even bankruptcy. The cost of litigation, recalls, and rebuilding customer trust can be substantial, highlighting the importance of maintaining proper food temperatures.
Recommended Food Storage Temperatures
Safe refrigerator temperature
To ensure the freshness and safety of perishable items, refrigerators should maintain a temperature below 41°F (5°C). By keeping foods chilled at this temperature, bacterial growth is slowed considerably, minimizing the risk of spoilage and foodborne illnesses. Regular monitoring of fridge temperatures is vital to ensure consistent performance.
Proper freezer temperature
Freezers should be maintained at or below 0°F (-18°C). At this temperature, the growth of bacteria and other pathogens is inhibited, preserving food quality and safety for extended periods. Proper packaging and labeling of frozen foods are also essential to maintain their integrity and prevent cross-contamination.
Guidelines for chilled display units
In establishments where chilled display units are used to showcase perishable items, the temperature should be maintained at or below 41°F (5°C). Regular monitoring and adjustment of the display unit’s temperature will help ensure the safety and appeal of the products on display.
Temperature Monitoring and Controls
Methods for monitoring food temperatures
There are various methods for monitoring food temperatures throughout the food production and handling process. Thermometers, both analog and digital, are commonly used to measure the temperature of cooked foods, chilled foods, and hot holding equipment. Continuous temperature monitoring systems equipped with alarms are also gaining popularity, providing real-time data to ensure prompt action.
Regular checks and maintaining records
Regular temperature checks are crucial to identify any deviations from safe temperature ranges. Staff should routinely record temperatures of perishable items, food storage areas, and cooking equipment to monitor compliance with temperature control guidelines. These records serve as evidence of due diligence and can be reviewed for quality control and during health inspections.
Corrective actions for temperature deviations
If a temperature deviation is detected, immediate corrective actions should be taken to mitigate the risk. For example, if a refrigerator’s temperature rises above the safe range, the affected food should be discarded, and the refrigerator fixed or replaced. Training staff on the appropriate response to temperature deviations is paramount to maintaining food safety standards.
Safe Food Handling Practices
Proper cooking and reheating temperatures
To kill harmful bacteria and ensure food safety, it is vital to cook foods thoroughly to their appropriate internal temperatures. Different foods have different minimum internal temperature requirements. For example, poultry should reach 165°F (74°C), while ground meat should reach 160°F (71°C) to eliminate pathogens effectively. Reheating leftovers should also be done to an internal temperature of at least 165°F (74°C).
Serving and holding temperatures
To prevent bacterial growth and maintain safe food temperatures during service or holding, hot foods should be kept at or above 135°F (57°C), while cold foods should be kept at or below 41°F (5°C). Buffet-style service should involve frequent temperature monitoring and replenishing of foods to ensure they remain within the safe temperature range.
Transportation temperature guidelines
Maintaining proper food temperatures during transportation is crucial to avoid compromising food safety. Cold foods should be transported in insulated coolers or refrigerated vehicles to keep them below 41°F (5°C). Hot foods should be transported in insulated containers to keep them at or above 135°F (57°C) until they are ready to be served.
Exceptions and Special Considerations
Specific foods with different temperature requirements
While most foods adhere to the temperature danger zone boundaries, some exceptions exist. For example, certain cheeses may require storage temperatures slightly above 41°F (5°C) to maintain their quality. It is essential to follow specific guidelines for such exceptions to ensure both food safety and product quality.
Variations for unique food preparation methods
Certain unique food preparation methods, such as sous vide cooking or low-temperature smoking, may require specific temperature ranges to achieve the desired results while maintaining food safety. It is crucial to follow established guidelines and regulations for these specialized techniques to minimize the risk of foodborne illnesses.
Critical control points in the food production process
Identifying critical control points in the food production process is critical for ensuring food safety. Temperature control is one such crucial aspect, and specific steps, such as cooking, cooling, and reheating, must be closely monitored and controlled. Implementing Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point (HACCP) principles can help identify and manage these crucial control points effectively.
Training and Education
Importance of staff training on temperature control
Proper training on temperature control is vital for all individuals involved in food handling. Staff should be educated on the principles of food safety, including the temperature danger zone, proper temperature monitoring techniques, and corrective actions. Regular training sessions and ongoing education help ensure that staff members are equipped to maintain the highest standards of food safety.
Food safety certification programs
Food safety certification programs, such as ServSafe, provide comprehensive training and education on various aspects of food safety, including proper temperature control. These programs offer in-depth knowledge, practical tips, and certificates upon successful completion, demonstrating an individual’s commitment to food safety best practices.
Continuous education and updates on regulations
Given the evolving nature of food safety regulations and best practices, continuous education and updates are crucial. Food establishments must stay up-to-date with the latest guidelines and regulations related to temperature control. Engaging in industry conferences, workshops, and regularly reviewing resources provided by regulatory authorities help ensure ongoing compliance and continuous improvement.
By understanding the temperature danger zone, adhering to best practices, and maintaining proper food temperatures, the risk of foodborne illnesses can be significantly minimized. Temperature control is a critical aspect of food safety, and it requires a collective effort from everyone involved in the food industry. Remember, keeping food within the safe temperature ranges is not just a requirement, but a vital responsibility to protect the well-being of consumers and the success of your business.